Understanding Mpox Disease: Symptoms and Prevention
Table of Contents
Mpox Disease: Did you know that over 30,000 people in more than 80 countries got mpox in 2022? This shows how important it is to know about this disease and how to stop it from spreading.
Mpox, also called monkeypox, is a disease that spreads from animals to humans. It started in Africa but has now spread worldwide, causing a big health issue.
We will look into what mpox is, its history, and its symptoms. We’ll also talk about how it spreads and how to prevent it. This will help keep people safe.
Key Takeaways
- Mpox, once called monkeypox, is a viral disease that has spread globally in 2022.
- It has a unique rash, fever, and flu-like symptoms. It spreads through close contact or touching infected things.
- To prevent it, use vaccines, wear protective gear, and isolate people who might be infected.
- Knowing the signs and how it spreads is key to stopping this disease.
- It’s vital to follow health advice to protect yourself and others from mpox.
What is Mpox Disease?
Definition and Overview
Mpox, also known as monkeypox, is a rare viral disease. It is caused by the monkeypox virus, part of the Orthopoxvirus genus. This illness is usually marked by a unique rash and flu-like symptoms. It was first found in 1958 in monkeys used for research, leading to its name.
History and Origins
The monkeypox virus likely started in Central and West Africa, where it lives in animals like rodents. The first human case was in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in 1970. Since then, outbreaks have happened in many African countries and a few other places, often from contact with infected animals.
Over time, the mpox virus has changed, leading to new versions and possibly different ways it spreads and affects people. The 2022 global outbreak made people worry more about its spread among humans. This highlights the need for better awareness, watching, and health steps to manage the disease.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1958 | First outbreaks of monkeypox reported in colonies of research monkeys |
| 1970 | First human case of monkeypox reported in the Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| 2022 | Global outbreak of mpox, leading to increased concern and public health response |
The mpox virus shows the challenges of zoonotic diseases and why we need to understand where they come from, how they change, and how they can spread between people. Scientists are studying this virus closely. The world is watching and working hard to stop future mpox outbreaks.
Symptoms of Mpox Disease
Mpox disease, also known as monkeypox, has symptoms that help identify it. Knowing these symptoms is key for early detection and managing the disease. Let’s look at the common signs of mpox disease.
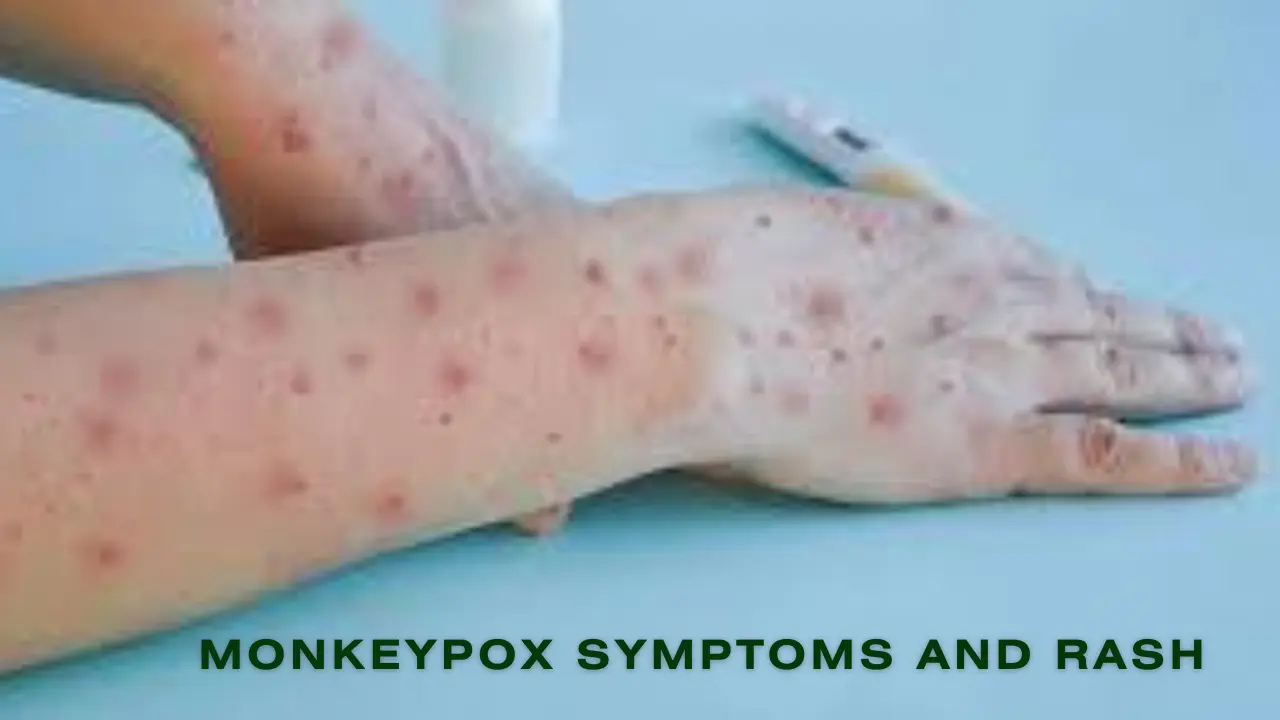
A key symptom of mpox is a rash. It starts as flat, red spots that turn into raised, fluid-filled blisters. These blisters can be on the face, hands, feet, or even inside the mouth.
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Backache
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fatigue
People with mpox may also have fever, headache, muscle aches, backache, swollen lymph nodes, and feel tired. These symptoms start 1-2 weeks after getting the virus and can last for days to weeks.
The severity of mpox symptoms can vary. Some people get a mild form, while others have severe cases. It’s important to see a doctor quickly for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Knowing the symptoms of mpox helps people recognize it. This way, they can prevent the virus from spreading and get medical help on time.
Mpox Disease Transmission
Mpox, also known as monkeypox, is a viral disease that spreads in different ways. Knowing how it spreads helps us prevent it and control its spread.
How Does Mpox Spread?
Mpox spreads through direct contact with infected people, their fluids, or contaminated items. It can enter your body through cuts, the lungs, or your eyes, nose, or mouth. It can also spread through close contact, like in relationships or when caring for someone who is sick.
People with mpox can spread it from the start of symptoms until their sores heal and the scabs fall off. Pregnant women can pass it to their babies through the placenta, causing birth mpox.
Risk Factors
Some things make you more likely to get mpox. These include:
- Close, intimate contact with an infected person
- Touching things touched by an infected person, like clothes or towels
- Living in or visiting places where mpox is common
- Going to big events or gatherings that increase your chance of getting it
- Having a weak immune system
Knowing how mpox spreads and who is at risk helps us protect ourselves and others.
| Transmission Mode | Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Direct contact with infected individualsContact with contaminated materialsRespiratory transmissionVertical transmission (from pregnant women to fetuses) | Close, intimate contact with infected personsExposure to contaminated materialsResiding in or traveling to areas with ongoing outbreaksParticipation in activities with increased risk of exposureCompromised immune system |
Understanding how mpox spreads and who is at risk helps us protect ourselves and our communities.
Diagnosis and Testing
Getting a correct diagnosis of mpox disease is key for treatment and stopping the spread. Doctors use different tests to find the mpox virus and rule out other illnesses with similar signs.
Diagnostic Methods
The main test for mpox is a lab test called a polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This test looks for the mpox virus genes in samples like skin, breath samples, or body fluids.
Doctors also do a physical check-up to look at symptoms and past health. This helps tell mpox apart from other skin rashes, like chickenpox or syphilis.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing to detect the mpox virus genetic material
- Physical examination and medical history review to evaluate symptoms and rule out other conditions
- Timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial for patient care and public health management
Quick and right diagnosis is key for giving the right medical care. It helps start isolation and public health steps to stop mpox from spreading.

Treatment Options
Managing mpox disease involves several steps. These steps aim to ease symptoms, help the body heal, and prevent more problems. There’s no cure for mpox, but there are ways to make it easier to handle and recover faster.
Symptom Management
The main goal is to ease the symptoms of mpox. Doctors might suggest over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen for fever, headaches, and body aches. They might also recommend topical creams or ointments for the skin lesions.
Antiviral Medications
In some cases, doctors might suggest antiviral drugs like tecovirimat (TPOXX) or brincidofovir. These can help fight the mpox virus and might lessen the illness’s severity and length. These drugs are usually for people with severe cases or a high risk of complications.
Supportive Care
Supportive care is also key in recovery. This includes:
- Drinking lots of fluids to stay hydrated
- Resting to let the body heal
- Keeping clean to stop the virus from spreading
- Seeing a doctor if symptoms get worse or new problems show up
It’s important to listen to your healthcare team and follow their treatment plan closely. This helps ensure the best recovery for mpox disease.
“Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to managing mpox disease and reducing the risk of complications.”
| Treatment Approach | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Symptom Management | Use of over-the-counter medications and topical treatments to alleviate symptoms | Moderate to high, depending on the severity of symptoms |
| Antiviral Medications | Prescription of tecovirimat (TPOXX) or brincidofovir to combat the mpox virus | High, particularly for severe cases or individuals at higher risk of complications |
| Supportive Care | Maintaining hydration, getting adequate rest, and practicing good hygiene | High, as it supports the body’s natural healing process |
Prevention Strategies
With the mpox disease outbreak, it’s vital to focus on prevention. Vaccination and personal protective measures are key. These steps help stop the virus from spreading.
Vaccination
The mpox vaccine is crucial for protecting people from the virus. It’s recommended for those at high risk, like close contacts of infected people and healthcare workers. The vaccine helps lessen symptoms and lowers the chance of passing it on.
Getting the full vaccine series is important for best results. If you have a weak immune system, you might need boosters. These keep you protected for a longer time.
Personal Protective Measures
- Avoid close, skin-to-skin contact with individuals who have mpox symptoms.
- Wear a well-fitted mask when in close proximity to others, particularly in crowded or poorly ventilated indoor settings.
- Practice good hand hygiene by frequently washing your hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
- Refrain from sharing personal items, such as towels, clothing, or bedding, with those who have been infected or are suspected of having mpox.
- Monitor your health and seek medical attention if you develop symptoms associated with mpox.
Combining vaccination with careful personal actions can greatly lower your risk of getting and spreading mpox. Stay informed and act early to help stop this health issue from getting worse.
| Prevention Measure | Effectiveness | Ease of Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccination | High | Moderate (requires access to vaccines) |
| Avoiding close contact | High | High |
| Wearing masks | Moderate | High |
| Practicing good hygiene | High | High |
Public Health Implications
The outbreak of mpox disease, once known as monkeypox, has caused big worries worldwide. Governments and health systems are acting fast to stop this new virus from spreading. In Singapore, they have set up strong systems to keep people safe.
The Singapore Ministry of Health is working with the World Health Organization (WHO) to watch the situation closely. They want to make sure everyone knows how to stay safe from mpox. They’re teaching people about the signs, how it spreads, and how to prevent it.
Healthcare places have everything they need to find, treat, and report mpox cases. The government is pushing for vaccination as a key way to fight mpox. People who can get the vaccine are told to do so, as it helps prevent getting very sick.
By using health policies and modern medicine, Singapore is trying to lessen the effects of this virus outbreak. They want to keep their citizens healthy and safe.
FAQ
What is Mpox disease?
Mpox, also known as monkeypox, is a viral infection caused by the monkeypox virus. It spreads from animals to humans.
What are the common symptoms of Mpox disease?
Symptoms include a skin rash, fever, headache, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes. Chills and exhaustion are also common.
How is Mpox transmitted?
It spreads through close contact with an infected person or contaminated materials. It can also come from animals to humans.
Who is at risk of contracting Mpox?
Those at risk include people who have close contact with infected individuals or animals. Travelers to areas with outbreaks are also at risk.
How is Mpox diagnosed?
Diagnosis is through tests like PCR, which detects the monkeypox virus in samples.
What are the treatment options for Mpox?
Treatment includes supportive care like pain relief and treating infections. In severe cases, antiviral medications might be used.
How can Mpox be prevented?
Prevention involves vaccination, good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected people, and proper protective gear when caring for patients.
What are the public health implications of Mpox?
Mpox outbreaks lead to increased surveillance and control measures. Strategies are developed to manage and contain the virus.




